
What is the benefit of vitamin b12?
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that your body can’t make on its own, so you need to get it from your diet or from supplements.
Vegetarians, people who are pregnant or nursing, and others who are at risk of deficiency may want to track their diets closely to make sure they’re getting enough.
Some medications can lower the effect of vitamin B12 in your body:
- Proton pump inhibitors. Example(Prilosec, Prevacid)
- H2 receptor antagonist (Zantac, Pepcid)
- Metformin
There are additional supplements available to get enough vitamin B12. Most of the B12 supplement’s content in dietary products is synthetic.
How Much to Get?
The answer depends on things including your age, your eating habits and medical conditions, and what medications you take.
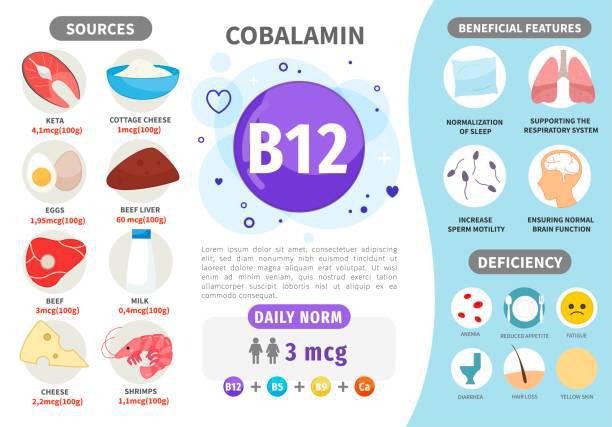
The average recommended amounts, measured in micrograms (mcg), vary by age:
- Infants up to age 6 months: 0.4 mcg
- Babies age 7-12 months: 0.5 mcg
- Children age 1-3 years: 0.9 mcg
- Kids age 4-8 years: 1.2 mcg
- Children age 9-13 years: 1.8 mcg
- Teens age 14-18: 2.4 mcg (2.6 mcg per day if pregnant and 2.8 mcg per day if breastfeeding)
- Adults: 2.4 mcg (2.6 mcg per day if pregnant and 2.8 mcg per day if breastfeeding)
Why is vitamin B12 essential?
The human body regularly needs vitamin B12 for proper functioning of the body. Vitamin B12 can also be obtained from the foods we eat. Inadequate vitamin B12 affects the growth of the body and creates some of the underlying symptoms.
Signs revealed when you are not getting enough vitamin B12 can be listed as,
- loss of appetite
- constipation
- weight loss
- numbness and tingling
- balance problems
- difficulty thinking
- confusion or memory problems
- dementia
- sore mouth or tongue
- Weakness, tiredness, or lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations and shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- A smooth tongue
- Constipation, diarrhea, loss of appetite, or gas
- Nerve problems like numbness or tingling, muscle weakness, and problems walking
- Vision loss
- Mental problems like depression, memory loss, or behavioral changes
A deficit of vitamin B12 perturbs the production of healthy red blood cells. Unhealthy cells die naturally before they involve in the production of new ones. This cycle leads to megaloblastic anaemia, also termed pernicious anaemia. Megaloblastic anaemia occurs if you do not eat enough foods that contain vitamin B12. You need to take vitamin B12 injections in case of a vitamin B12 deficit.
Common symptoms of anaemia
- decreased appetite
- diarrhea
- weakness
- paleness
- extreme fatigue
- irritability
Vitamin B12-rich fruits
Most of the fruits do not contain vitamin B12. Most of the fruits are high in folic acid. Therefore, vitamin B12 content is less in fruits.
- Apple
- Banana
- Blueberries
- Orange
Vitamin B12 rich dry fruits
Good sources of vitamin B12 also include dry fruits. Almonds and peanuts have strong vitamin B12 content.
Vitamin B12-rich vegetables
- Alpha Alpha
- Beetroot
- Butternut squash
- Mushroom
- Potato
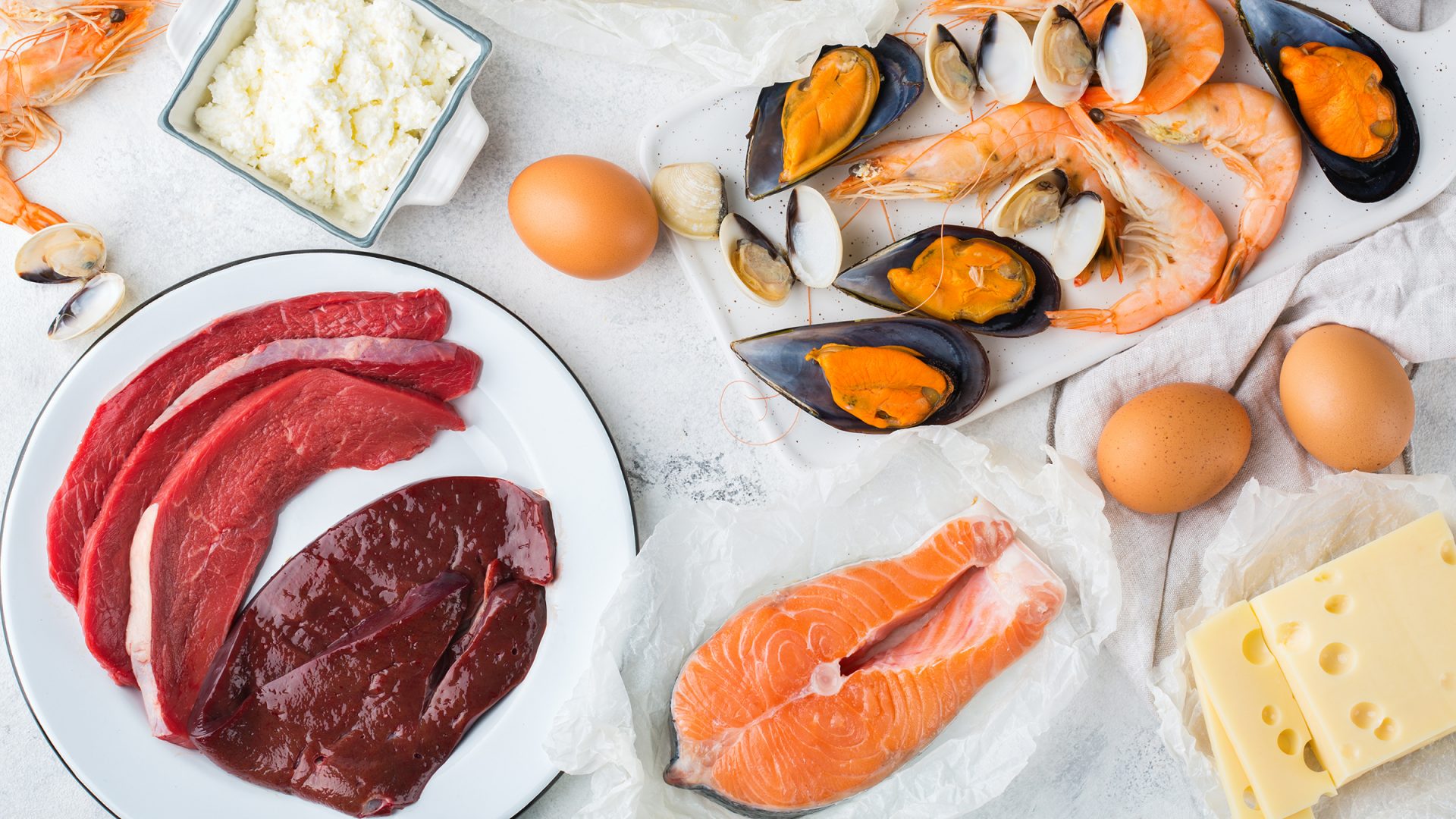
12 Foods That Are High in Vitamin B12
- Animal liver and kidneys
- Clams
- Sardines
- Beef
- Fortified cereal
- Tuna
- Fortified nutritional yeast
- Trout
- Salmon
- Fortified nondairy milk
- Milk and dairy products
- Eggs
Safety and side effects
When taken at appropriate doses, vitamin B-12 supplements are generally considered safe. While the recommended daily amount of vitamin B-12 for adults is 2.4 micrograms, higher doses have been found to be safe. Your body absorbs only as much as it needs, and any excess passes through your urine.
High doses of vitamin B-12, such as those used to treat a deficiency, might cause:
- mild diarrhea
- itching
- skin rash
- headache
- dizziness
- nausea
- vomiting
- pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure early in treatment
- vein thrombosis
- sensation of swelling
- polycythemia vera (rare, slow growing blood cancer)
Reference: mayoclinic.org, healthline.com, www.starhealth.in, www.webmd.com
